선형 자료구조 연결리스트
선형 자료구조 연결리스트
연결리스트란 순차 자료구조와 다르게 물리적 순서가 유지되지 않는다 저장을 다른 위치에하기 때문에 서로를 연결시킬 링크가 필요하다
연결 리스트
- 자료의 논리적인 순서와 물리적 순서가 일치하지 않는다(순서를 맞추기위한 오버헤드 발생x)
저장공간을 유연하게 사용할 수 있어서 메모리를 효율적으로 사용
- 연결 방식에 따라 단순 연결리스트, 원형 연결리스트, 이중 연결리스트, 이중 원형 연결리스트
연결리스트의 노드
<원소(data), 주소(link)>의 구조를 가지고 있다
- 데이터 필드
- 원소의 값을 저장
- 저장할 원소의 형태에 따라서 하나 이상의 필드로 구성
- 링크 필드
- 다음 노드의 주소를 저장
- 포인터 변수를 사용해서 주소값을 저장한다

단순 연결리스트 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXSTRLEN 16
// 단순 연결 리스트의 노드 구조를 구조체로 정의
typedef struct _LISTNODE_ { //자기참조 구조체
int data;
struct _LISTNODE_* next;
} LISTNODE;
// 리스트의 시작을 나타내는 head 노드를 구조체로 정의
typedef struct _LINKEDLIST_ {
LISTNODE* head;
int numOfData;
} LINKEDLIST;
/*
* 연결 리스트 초기화, dummy head 노드 메모리 할당
*/
void InitList(LINKEDLIST* pList)
{
pList->head = (LISTNODE*)calloc(1, sizeof(LISTNODE));
pList->head->next = NULL;
pList->numOfData = 0;
}
/*
* 연결 리스트 메모리 해제
*/
void FreeList(LINKEDLIST* pList)
{
LISTNODE* pre = pList->head;
LISTNODE* cur = pList->head->next;
while (cur != NULL)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(pre);
pre = NULL;
}
free(pList->head);
pList->head = NULL;
}
/*
* 리스트의 만앞(head노드가 가리키는 첫번째 노드)에 새로운 노드 추가
*/
void InsertFirst(LINKEDLIST* pList, int x)
{
LISTNODE* newNode = NULL;
newNode = (LISTNODE*)calloc(1, sizeof(LISTNODE));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->next = pList->head->next;
pList->head->next = newNode;
pList->numOfData += 1; // 데이터 수 증가
}
/*
* 리스트의 마지막에 새로운 노드 추가
*/
void InsertLast(LINKEDLIST* pList, int x)
{
LISTNODE* pre = NULL;
LISTNODE* cur = NULL;
LISTNODE* newNode = NULL;
newNode = (LISTNODE*)calloc(1, sizeof(LISTNODE));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
pre = pList->head;
cur = pList->head->next; // head는 초기화 과정에서 dummy로 만들어주었으므로, head->next 부터 순회
while (cur != NULL)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
//newNode->next = NULL; // NULL임
newNode->next = pre->next; // NULL 임
pre->next = newNode;
pList->numOfData += 1; // 데이터 수 증가
}
/*
* data x를 가진 노드 리스트에서 찾아서 주소 반환
*/
LISTNODE* SearchNode(LINKEDLIST* pList, int x)
{
LISTNODE* cur = NULL;
cur = pList->head->next;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return cur;
}
/*
* targer 노드를 리스트에서 삭제
*/
void DeleteNode(LINKEDLIST* pList, LISTNODE* target)
{
LISTNODE* pre = NULL;
LISTNODE* cur = NULL;
if (pList->head->next == NULL || target == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error, null pointer\n");
return;
}
else
{
pre = pList->head;
cur = pList->head->next;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur == target)
{
pre->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
pList->numOfData -= 1;
}
/*
* list의 정보를 출력
*/
void PrintList(LINKEDLIST* pList)
{
LISTNODE* cur = NULL;
cur = pList->head->next;
printf("L = (");
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
if (cur != NULL)
{
printf(", ");
}
}
printf(")\n");
}
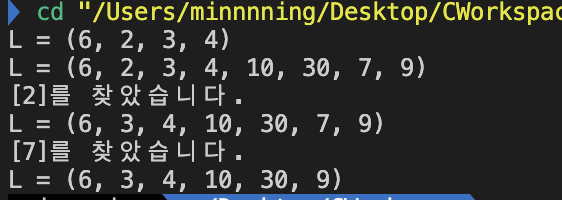
int main()
{
LINKEDLIST list;
LISTNODE* find = NULL;
InitList(&list);
InsertFirst(&list, 4);
InsertFirst(&list, 3);
InsertFirst(&list, 2);
InsertFirst(&list, 6);
PrintList(&list);
InsertLast(&list, 10);
InsertLast(&list, 30);
InsertLast(&list, 7);
InsertLast(&list, 9);
PrintList(&list);
find = SearchNode(&list, 2);
if (find == NULL) printf("찾는 데이터가 없습니다.\n");
else printf("[%d]를 찾았습니다.\n", find->data);
DeleteNode(&list, find);
PrintList(&list);
find = SearchNode(&list, 7);
if (find == NULL) printf("찾는 데이터가 없습니다.\n");
else printf("[%d]를 찾았습니다.\n", find->data);
DeleteNode(&list, find);
PrintList(&list);
FreeList(&list);
return 0;
}
원형 연결리스트
단순 연결리스트에서 마지막 노드는 null을 가리킨다 이 마지막 노드의 null을 첫 노드의 주소로 바꾸면 원형 연결리스트가 된다
- 링크를 따라가면 계속 순회 가능
- 마지막을 알려면 null 대신 head가 가리키는 주소와 비교해야 한다 head는 항상 첫번째 노드를 가리킨다
이중 연결리스트
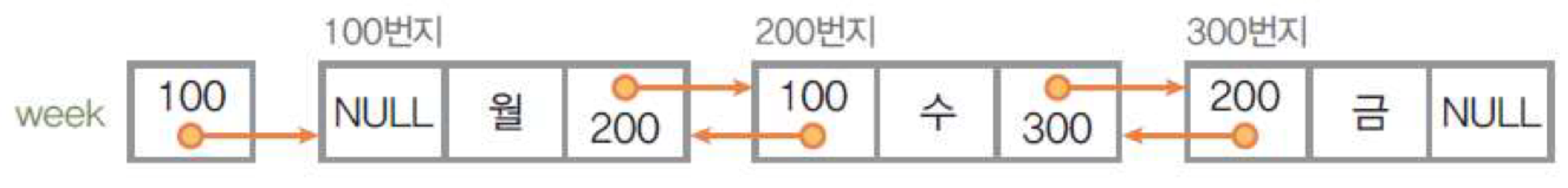
- 링크가 양쪽으로 생긴다
- 따라서 꼭 head에서 시작하지 않아도 된다
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.